Rig level access
Rig Level Access is a permission management feature designed to give administrators more granular control over what users can see and do within RigBridge. It’s especially useful for customers who don't have a team-based access system in place. With this feature, access can be restricted by rig, ensuring users only see data relevant to their assigned rigs.
This feature is primarily for system administrators and super admins who manage access permissions through the System Configuration Tool.
How it looks
Rig Level Access adds a new layer of control in System Configuration Tool by associating each node (such as projects, sections, and wells) with a rig. Permissions are then filtered at every level based on the user's assigned roles and associated rigs.
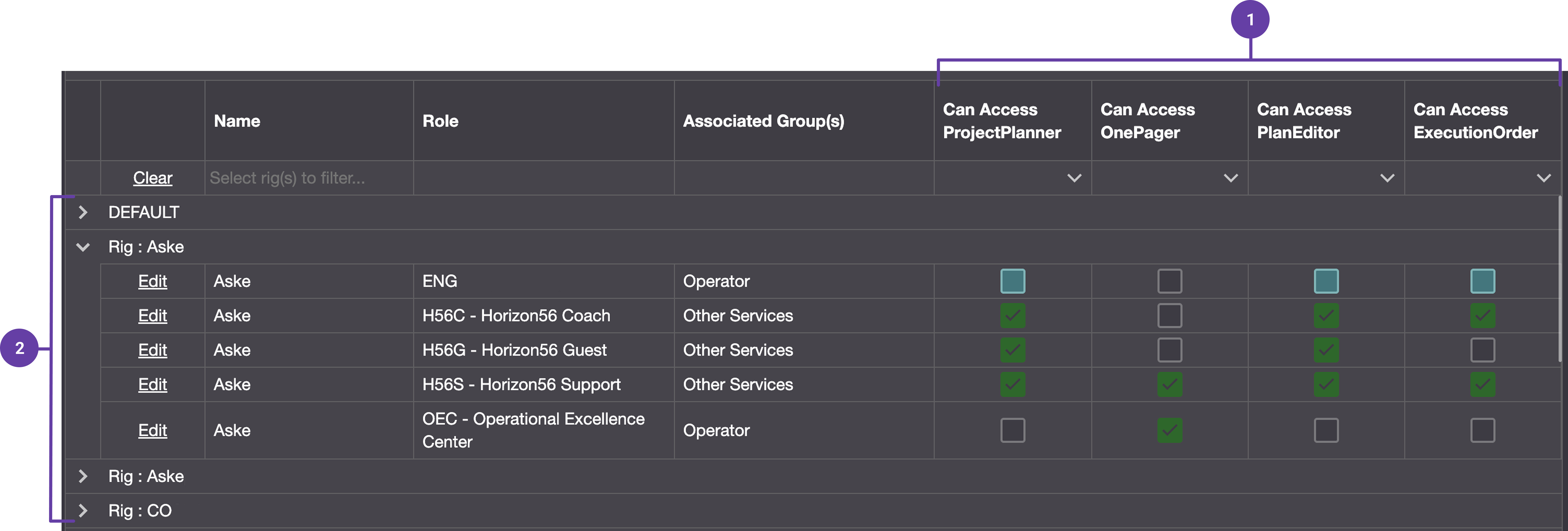
Permission matrix: Permission Keys are set and typically specified with Can Access (read) and Can Manage (edit).
Hierarchy mapping: The system uses mapping logic to link permissions with rig nodes, based on customer-specific hierarchies.
Important
Access is automatically filtered in Plan Overview, Rig Configuration, and Fleet overview based on the user’s rig access.
Step-by-step instructions
Access the Permissions matrix in System Configuration Tool: Access System Configuration Tool and navigate to the permission matrix.
Manage default permissions: Roles are pre-defined with specific permissions. This allows mass inheritance across all rigs, and you can uncheck them for specific rigs where it shouldn't apply. Read more about grouped permissions here: Permissions.
Assign permissions on specific rigs: Permissions are tied to the role-rig combination, not the individual user. Locate the specific rig and role you want to update, click the edit link, and check or uncheck the permission boxes. Read more about it here: Step-by-step instructions.
Examples
A user working on Rig A is given “DSV” access. They can see and edit everything on that rig, but only view top-level nodes on any other rig where they hold a “Guest” role.
If “Can Access Plan Editor” is added to the default DSV role, it becomes available to all rigs unless explicitly disabled for certain rigs.
Tips and tricks
Use the default role setup for efficiency. It reduces manual configuration when dealing with multiple rigs.
Be cautious when assigning high-level permissions; these grant broad control and should typically be reserved for internal operator roles.
For third-party service providers, assign only the necessary permissions tied to the specific rigs they work on.
Troubleshooting
Unexpected data visibility: Check if the project is linked to multiple rigs or if default roles are overly permissive.